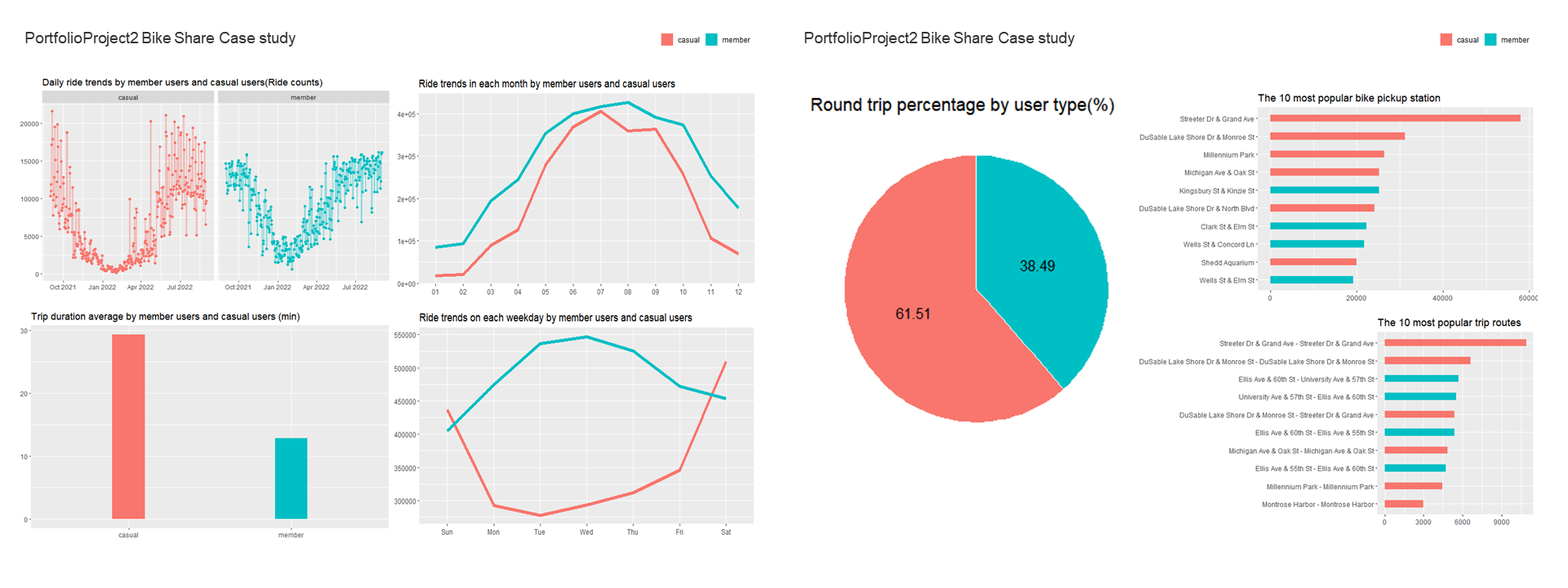
Data Source & Purpose of Data Analysis
Data Source: Divvy Bikes license
Purpose of Data Analysis
- How Does a Bike-Share Navigate Speedy Success?
- How can we convert casual riders into members?
- How annual members and casual riders differ?(When and where do they ride?)
If you want to see this project as a HTML document from R Markdown, please click this Link If you want to see this project as a PDF document from R Markdown, please click this Link
1. Prepare Data
1.1 Install Packages
install.packages("tidyverse", repos = "http://cran.us.r-project.org")
library(tidyverse)
install.packages("lubridate", repos = "http://cran.us.r-project.org")
library(lubridate)
install.packages("ggplot2", repos = "http://cran.us.r-project.org")
library(ggplot2)1.2 Import Data
#Import datasets from Sep 2021 to Aug 2022 and bind them all
filepath <- "data/202109-divvy-tripdata.csv"
new_dataset <- read.csv(filepath)
repeat{
dateofdata <- as.integer(substr(filepath, 6, 11))+1
substr(filepath, 6, 11) <- as.character(dateofdata)
second_import <- read.csv(filepath)
new_dataset <- rbind(new_dataset, second_import)
if(dateofdata == 202112){
filepath <- "data/202201-divvy-tripdata.csv"
second_import <- read.csv(filepath)
new_dataset <- rbind(new_dataset, second_import)
}else if(dateofdata == 202208){
break
}
}2. Process Data
2.1 Create subsets
#Prepare a dataset to inspect its datetime data
dt_dataset <- select(new_dataset, 'ride_id', 'started_at', 'ended_at', 'member_casual')
#Prepare a dataset to inspect geographic data
lc_dataset <- select(new_dataset, 'ride_id', 'start_station_name', 'end_station_name', 'member_casual')2.2 Organize and Clean Data
- Convert the date columns from character to date type.
- Extract the month column and wday column from the date column.
- Reorder the weekdays, because it's not in the right order.
- Convert the started_at, ended_at columns to time type.
- Calculate the trip duration using the converted time columns.
- Remove bad data which contains negative time difference from trip duration column.
- Deal with missing values.
- Concatenate start and end station names to observe trip routes.
#Data cleaning for dt_dataset
#Convert Character to Date and format to Month and Weekday
dt_dataset$trip_date <- as.Date(dt_dataset$started_at)
dt_dataset$trip_month <- format(as.Date(dt_dataset$trip_date), "%m")
dt_dataset$trip_wday <- format(as.Date(dt_dataset$trip_date), "%a")
#Reorder the weekdays
dt_dataset$trip_wday <- factor(dt_dataset$trip_wday, levels= c("Sun", "Mon", "Tue", "Wed", "Thu", "Fri", "Sat"))
#Convert Datetime to Time datatype, remove rows with negative trip_duration
dt_dataset$trip_stime <- as.POSIXct(dt_dataset$started_at, tz='UTC')
dt_dataset$trip_etime <- as.POSIXct(dt_dataset$ended_at, tz='UTC')
dt_dataset$trip_duration <- difftime(dt_dataset$trip_etime, dt_dataset$trip_stime)
dt_dataset2 <- subset(dt_dataset, trip_duration>0)
#Data Cleaning for lc_dataset
#Deal with missing Values
lc_dataset <- lc_dataset %>%
filter(start_station_name!=""&end_station_name!="")
#Create trip_route column by concatenating the start and end station names
lc_dataset$trip_route <- paste(lc_dataset$start_station_name, lc_dataset$end_station_name, sep=" - ")
#Create round trip column by inspecting whether start station name equals to end station name or not
lc_dataset$round_trip[lc_dataset$start_station_name==lc_dataset$end_station_name] <- "YES"
lc_dataset$round_trip[lc_dataset$start_station_name!=lc_dataset$end_station_name] <- "NO"3. Analyze Data
3.1 Daily Bike Ride Trends
#Comparison by the number of daily ride between user types
dt_dataset2 %>%
group_by(trip_date, member_casual) %>%
summarize(daily_ride_count=n_distinct(ride_id)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = trip_date, y = daily_ride_count, color = member_casual)) +
geom_point() +
geom_line(aes(col=member_casual), size=1, alpha=0.4) +
facet_wrap(~member_casual) +
labs(title="Daily ride trends by member users and casual users(Ride counts)") +
theme(axis.title.x=element_blank(), axis.title.y=element_blank(), legend.position="none")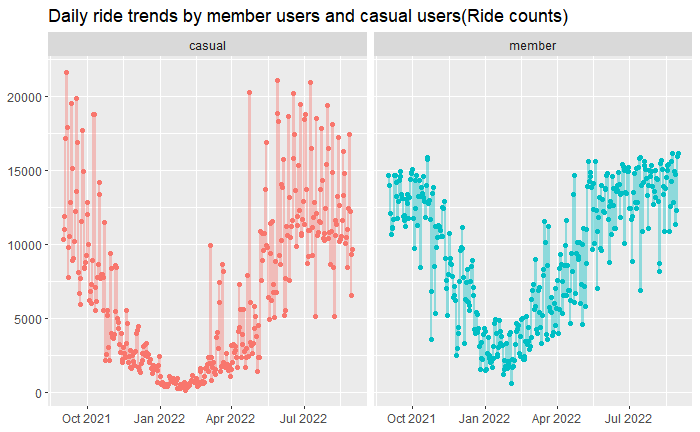
3.2 Bike Ride Tendency by each weekday
#Compare the number of ride by each user type every weekdays
dt_dataset2 %>%
group_by(trip_wday, member_casual) %>%
summarise(ride_count_by_weekdays=n_distinct(ride_id)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=trip_wday, y=ride_count_by_weekdays, group=member_casual)) +
geom_line(aes(color=member_casual), size=2) +
labs(title="Ride trends on each weekday by member users and casual users") +
theme(axis.title.x=element_blank(), axis.title.y=element_blank(), legend.position="bottom", legend.title = element_blank())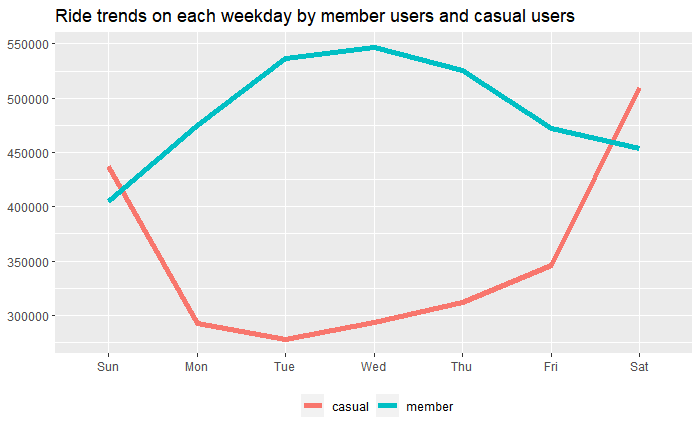
3.3 Bike Ride Tendency by each month
#Compare the number of ride by each user type every months
dt_dataset2 %>%
group_by(trip_month, member_casual) %>%
summarise(ride_count_by_months=n_distinct(ride_id)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=trip_month, y=ride_count_by_months, group=member_casual)) +
geom_line(aes(color=member_casual), size=2) +
labs(title="Ride trends in each month by member users and casual users") +
theme(axis.title.x=element_blank(), axis.title.y=element_blank(), legend.position="bottom", legend.title = element_blank())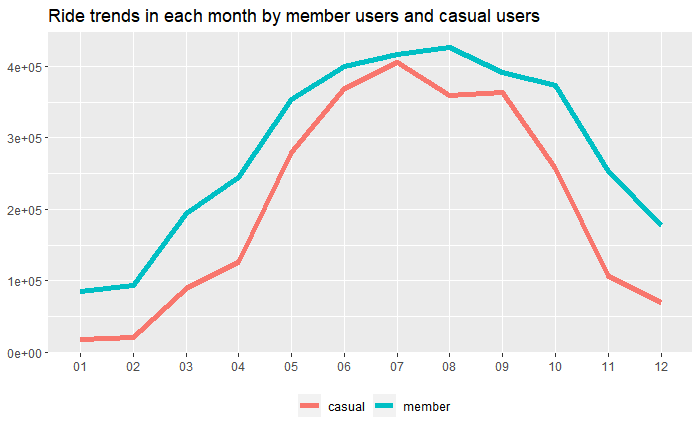
3.4 Average Trip Duration
#Compare the average trip duration between the two user types
dt_dataset2 %>%
group_by(member_casual) %>%
summarise(trip_duration_average=mean(as.integer(trip_duration)/60)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=member_casual, y=trip_duration_average, fill=member_casual)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", width=0.2) +
labs(title="Trip duration average by member users and casual users (min)") +
theme(axis.title.x=element_blank(), axis.title.y=element_blank(), legend.position="none")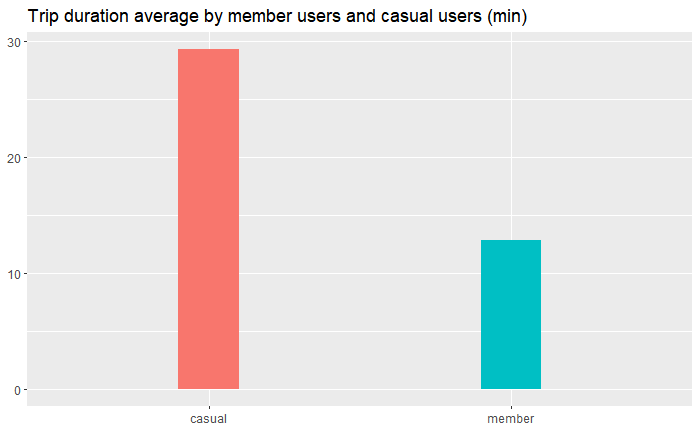
3.5 Round Trip User Proportion
#Create the pie chart to see the proportion of each user type from all the round trips
lc_dataset %>%
filter(round_trip=="YES") %>%
group_by(member_casual) %>%
summarize(count=n_distinct(ride_id)) %>%
mutate(percent=count/sum(count)*100) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = 2, y = percent, fill = member_casual)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", color = "white") +
coord_polar(theta = "y", start = 0) +
labs(title="Round trip percentage by user type(%)") +
geom_text(aes(label = round(percent,2)), position = position_stack(vjust = 0.5), color = "black") +
theme(axis.text = element_blank(),
axis.ticks = element_blank(),
axis.title = element_blank(),
panel.grid = element_blank(),
panel.background = element_blank(),
plot.background = element_blank(),
legend.position="bottom",
legend.title = element_blank())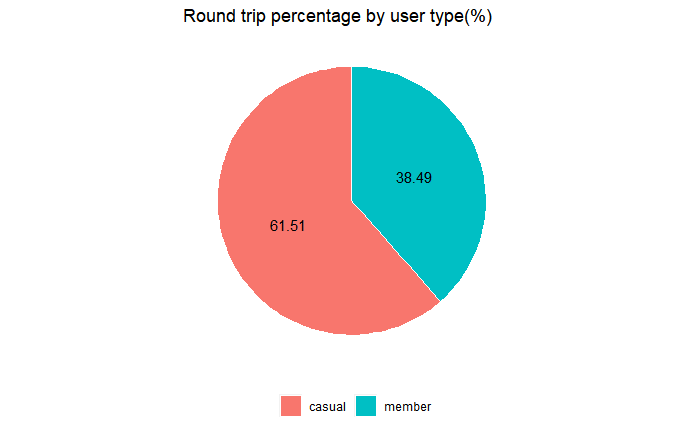
3.6 The 10 Most Popular Trip Route
#Check the 10 most popular trip routes
lc_dataset %>%
group_by(member_casual, trip_route) %>%
summarise(count=n_distinct(ride_id)) %>%
arrange(desc(count), trip_route) %>%
head(n=10) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=count, y=reorder(trip_route, count), fill=member_casual)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", width=0.4) +
labs(title="The 10 most popular trip routes") +
theme(axis.title.x=element_blank(), axis.title.y=element_blank(), legend.position="bottom", legend.title = element_blank())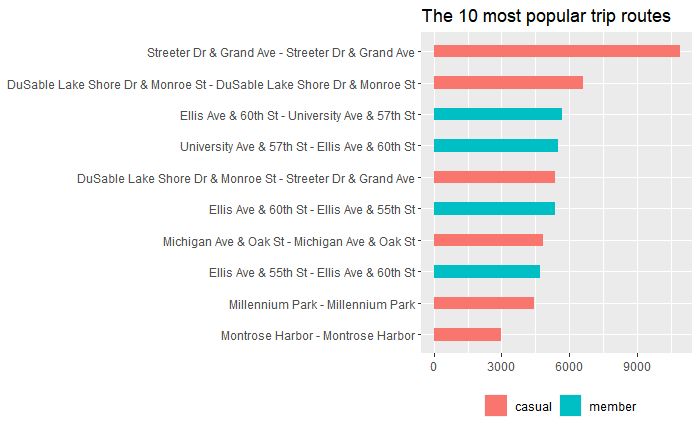
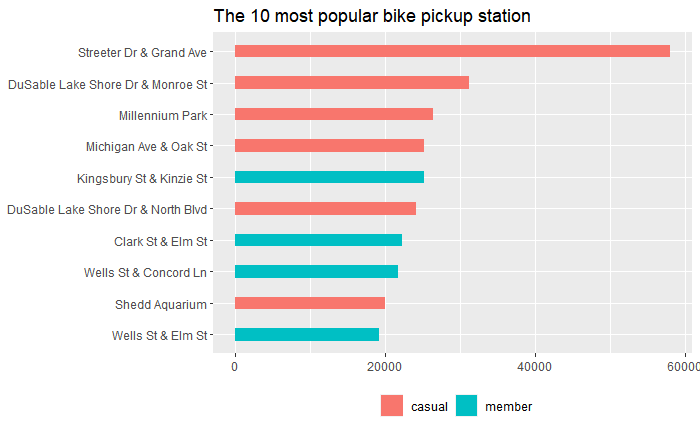
3.7 The 10 Most Popular Pickup Station
#Create the bar chart to see the top 10 popular station to start the trip
lc_dataset %>%
group_by(start_station_name, member_casual) %>%
summarize(ride_count=n_distinct(ride_id)) %>%
arrange(desc(ride_count)) %>%
head(n=10) %>%
ggplot(aes(x=ride_count, y=reorder(start_station_name, ride_count), fill=member_casual)) +
geom_bar(stat = "identity", width=0.4) +
labs(title="The 10 most popular bike pickup station") +
theme(axis.title.x=element_blank(), axis.title.y=element_blank(), legend.position="bottom", legend.title = element_blank())